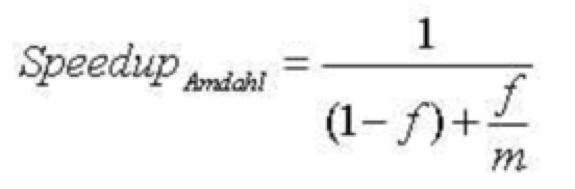Litecoin price declined further and moved below the $120 level against the US Dollar. LTC/USD is likely to decline further and it may even test the $100 level.
Key Talking Points
Litecoin price fail to move higher and it declined below the $120 level (Data feed of Kraken) against the US Dollar.
This week’s highlighted key bearish trend line with current resistance near $125 is still in place on the hourly chart of the LTC/USD pair.
The pair is likely to extend declines and it may accelerate declines toward $100.
Litecoin Price Forecast
There on litecoin price as it fell further from the $130 swing high against the US dollar. The LTC/USD pair declined and cleared the $120 support level, which opened the doors for more losses.
The pair even broke the $110 level and it formed a low at $109. At the moment, the price is correcting higher above $100 with a tiny bullish bias. An initial resistance is close to the 23.6% Fib retracement level of the downside move from the $139 high to $109 low.
It seems like the price may correct in the short term, but the broken support at $120 may act as a hurdle. Moreover, this week’s highlighted key bearish trend line with current resistance near $125 is still in place on the hourly chart of the LTC/USD pair.
Lastly, the 50% Fib retracement level of the downside move from the $139 high to $109 low is near the same trend line resistance to act as a barrier for gains. Only a close above the $125 and $130 resistance levels could open the doors for an upside recovery.
On the downside, the recent low of $109 is a tiny support. Once there is a break below the $109 level, the price will most likely test the $100 level. Below the mentioned $100 level, there could be heavy downsides.
The overall technical structure is negative as long as the price is below $140.
Trade safe traders and do not overtrade!
The post appeared first on .
The HireGo marketplace will deploy three smart contracts to the Ethereum network: theHGOtoken, a Vehicle non-fungible token and a Rental contract. An additional storagecontract will be deployed for use in a hub-and-spoke model, ensuring that any updates orbugfixes may be released in a timely manner, without loss of data.
HGOTokenThe in-app currency is theHGOtoken, a cryptocurrency conforming to the ERC20 standard.There will be a total of 100,000,000 tokens created, of which 60% are being allocated foran initial coin offering. Each token will be divisible by 18 decimal places. Any valueexchange on the HireGo marketplace will be conducted using theHGOtokens.
블록체인이 실제 상용 서비스를 제공하는 데에 있어 가장 큰 장애물은 트랜잭션 속도가 낮다는 것입니다. 이러한 몇몇 트랜잭션이 몇 분 또는 몇 시간씩 걸리는 문제를 이전의 중앙화된 컴퓨팅시스템에서는 고성능 마이크로 프로세서로 해결하려고 하려고 하였습니다. 이는 컴퓨팅 서비스가 제공 할 수 있는 가능성을 제한합니다. 다행스럽게도, 컴퓨터 과학자들은 컴퓨팅 성능을 효율적으로 향상시키는 기술을 이미 사용하고 있는데 그 기술이 바로 병렬 처리기술 입니다.
aelf는 독립적인 트랜잭션을 위해 병렬 처리를 사용합니다.
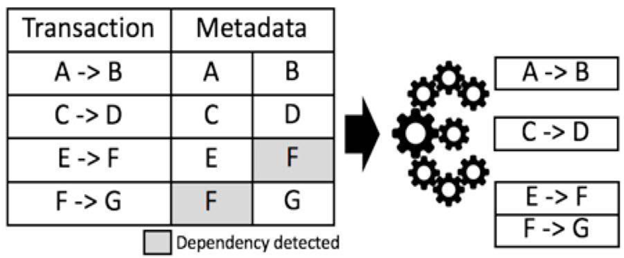
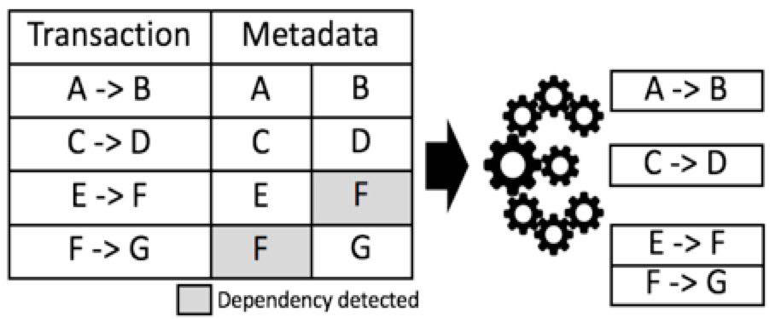
1. aelf는 정적 트랜잭션 상태를 분석하고 각 트랜잭션의 영향을 받은 데이터 범위를 평가합니다. 아래 그림에서 볼 수 있듯이 읽기/쓰기 충돌이 없는 트랜잭션 들은 각 트랜잭션의 출력에 영향을 미치지 않는 여러 그룹으로 분류 할 수 있습니다
2. 블록이 형성되는 과정 중에, 노드는 트랜잭션의 뮤텍스(mutex)를 기반으로 다른 그룹에 트랜잭션을 할당합니다. 그룹 내 트랜잭션은 순차적으로 처리되며 모든 그룹의 트랜잭션은 동시에 처리됩니다.
3. 다른 트랜잭션이 처리되는 동안 데이터 범위가 변경되는 영향을 받는 특수 트랜잭션의 경우, 노드는 병렬로 처리 할 수 있는 트랜잭션의 우선 순위를 결정합니다. 충분한 거래 수수료가 있으면 비 병렬 그룹의 특수 트랜잭션이 순서대로 처리됩니다.
병렬 처리는 Amdahl의 법칙에 의해 명료하게 설명 될 수 있습니다.
(f : 향상되는 시스템의 비율(%), m : 성능향상 index)
Amdahl의 법칙에 따르면 전체 작업의 성능(속도)은 시스템 리소스의 개선과 함께 증가하지만 이론적인 성능(속도) 향상이 시스템 개선에 관계없이 제한되는 구간이 존재합니다.
대부분의 계좌(account)간 트랜잭션은 뮤텍스(mutex) 이므로 병렬처리가 가능합니다. 그러나 기존의 블록체인 기술은 데이터를 순서대로 처리하므로 많은 컴퓨팅 리소스가 낭비됩니다. EVM(이더리움 가상머신)을 예로 들면, 모든 데이터 및 수요 가스 요금에 대해 순차적 처리를 사용하기에 처리 효율이 낮습니다.
aelf는 컴퓨팅 파워가 증가함에 따라 스케일링(확장성)이 가능하게 합니다.
데이터 처리 속도 자체만을 최적화하는 것이 궁극적인 목표는 아닙니다. 병렬 처리의 중요성은 확장성에 대한 잠재력에 있습니다.
우리는 모두 이더리움의 확장성이 이슈가 되어 화두에 올랐던 것을 알고 있습니다. 문제는 이더리움의 오직 한 노드가 트랜잭션을 순차적으로 처리 할 수 있다는 사실에 있습니다. 따라서 이더리움의 전체 처리 속도는 가장 느린 노드에 의해 제한됩니다.
코스모스는 간단한 솔루션을 제공합니다 : “한 영역에서 너무 많은 사람들이 사용하여 트랜잭션 속도가 느려지는 경우 허브에 다른 영역을 추가하고 해당 영역을 통해 사용자의 절반이 이용하도록 지시하여 트랜잭션 속도가 두 배가됩니다”
그러나 더 많은 컴퓨팅 파워가 추가되었음에도 영역당 트랜잭션 처리의 효율성은 여전히 제한적입니다.
aelf는 트랜잭션을 처리하는데 있어 클라우드 컴퓨팅을 도입했습니다. aelf의 자체 커널은 각 노드가 컴퓨터 클러스터에서 작동 할 수 있게 합니다. 이것은 더 많은 컴퓨팅 파워가 aelf 에코 시스템에 합류하면 시스템 보안성을 향상 시킬 뿐만 아니라 트랜잭션 속도를 컴퓨팅 파워에 비례하여 증가 시킨다는 것을 의미합니다. 그림에서 볼 수 있듯이, aelf 그룹의 읽기 / 쓰기 충돌 없이 일어난 트랜잭션을 서로 다른 카테고리로 분류하고, 서로 다른 트랜잭션 그룹을 동시에 처리합니다.
그러나 스케일링은 다양한 주제입니다. 인센티브 메커니즘 및 합의 메커니즘을 통해 확장성(scaling)을 가장 효과적으로 달성 할 수 는 방법에 대해 생각해 볼 가치가 있습니다. aelf의 토큰 디자인과 컨센서스는 이 분야에서 흥미로운 연구가 될 것 같습니다. 그리고 그것이 이 시리즈의 다음 주제가 될 것 입니다.
자세한 내용은 공식 웹 사이트를 방문하거나 텔레그램에서의 실시간 토론에 참여하세요!
공식 웹사이트 :
텔래그램 : korean
또는,
Facebook:
——————————————————————————————————–
v
One of the biggest obstacles for Blockchains serving the real business world is its low transaction speed. This situation has been seen in centralised computing systems in the past where certain transactions may take minutes or hours to solve with powerful microprocessors. This limits the possibility of what computing services can serve. Fortunately, computer scientists have been using an efficient approach to improve computing performance: parallel processing.
aelf: Parallel processing to handle commercial-scale transactions and possibilities for scaling
One of the biggest obstacles for Blockchains serving the real business world is its low transaction speed. This situation has been seen in centralised computing systems in the past where certain transactions may take minutes or hours to solve with powerful microprocessors. This limits the possibility of what computing services can serve. Fortunately, computer scientists have been using an efficient approach to improve computing performance: parallel processing.
aelf uses parallel processing for independent transactions
1. aelf analyzes the static state of transactions and assesses the impacted data range of each transaction. As illustrated in the Figure, transactions without read/ write conflicts can then be categorised in different groups, each not affecting the output of each transaction.
2. During the process of Block formation, nodes assign transactions to different groups based on mutex of the transactions. Transactions within a group will adopt sequential processing, while all groups will be processed simultaneously.
3. For special transactions whose impacted data range changes while other transactions are being processed, nodes will prioritize transactions that can be processed in parallel. With sufficient transaction fees, these special transactions in a non-parallel group will be processed in sequence. Otherwise nodes can reject to process these transactions.
Parallel processing can be fairly explained by Amdahl’s law.
The law shows that the execution of the whole task increases with the improvement of the resources in the system and that regardless of the magnitude of the improvement, the theoretical speedup is always limited by the part of the task that cannot benefit from the improvement.
Most of the transactions between accounts are mutex, thus can be processed in parallel. However, existing Blockchain technologies process data in sequence, leaving a large amount of computing resources wasted. Take EVM as one example, it adopts sequential processing for all the data and demand gas fees, resulting in low processing efficiency.
aelf enables scalable performance as computational power increases
Optimizing data processing speed itself is not the ultimate goal. The significance of parallel processing is the potential for scalability.
We have all seen the heated debate on the scalability of Ethereum. The difficulty lies in the fact that one node on Ethereum can only process transactions in sequence. Thus the whole processing speed of Ethereum is limited by the slowest node.
Cosmos provides a straightforward solution — — “if your transaction speed slows in one zone because too many people are using it, you simply add another zone to the hub and direct half the users over that zone, thereby doubling your transaction speed”. However, the efficiency of processing transactions per unit is still limited even when more computing power was added.
aelf introduces cloud computing in processing transactions. The aelf Kernel enables each node to operate on a cluster of computers. This means when more computational power joins the aelf eco-system, it not only enhances system security but also grows transaction speed proportionally. As illustrated in the figure, aelf groups transactions without read/write conflict into different categories, and then process different groups of transactions simultaneously.
Scaling, however, is a multidimensional subject. It is worth thinking about how scaling can be best achieved through an incentive mechanism and consensus mechanism. aelf’s token design and consensus is likely to provide an interesting exploration in the field. And this will be the next topic for this series articles.
While stabilizing the core we are also planning the next steps. The Kernel is going to be run in a computing cluster (numerous computers together in the same network). As said earlier one of the roles of the Scheduler is to send transactions to be executed by worker machines. In order for this to work we need to design and implement the network layer and the communication protocol for in-cluster communication.