As shown in the two graphs at left, our compact block is slightly larger than ’s compact block. The compact block is always propagated immediately to their neighbors.
For the newly proposed transactions, if some of them are missing in your transaction pool, they can be propagated after you send out the compact block. Those are parallel process and don’t affect each other, those transactions are verified and propagated and to the next neighbor.
You may ask:
What if a miner refuses to provide the complete version of proposed transactions?
This will not affect block propagation because blocks are propagated regardless of whether there are fresh transactions in their transaction proposal zone. The other miners will still proceed with because there are enough proposed transactions to confirm.
What if miners incorporate these proposed-without-broadcast transactions in their later blocks to gain a de facto selfish advantage?
In NC, the advantage in slow block propagation is always useful in finding the next block. For miners, they can only tell the block header and transfer the block really slowly after they find a block, during this process you are the only one who can mine the block.
However, In NC-Max, it can only be used to slow down propagation n block afterward, but only if that block is found by the attacker. Because this propagated without broadcast transactions, only the selfish miners know those transactions, and only the selfish miner can use it as an advantage. However, it can not be used in the next block because there needs to be a gap.
A miner can only mine transactions that are proposed between 2 or 5 blocks before that, you can not mine a transaction proposed in the previous block, but only if that block is found by an attacker.
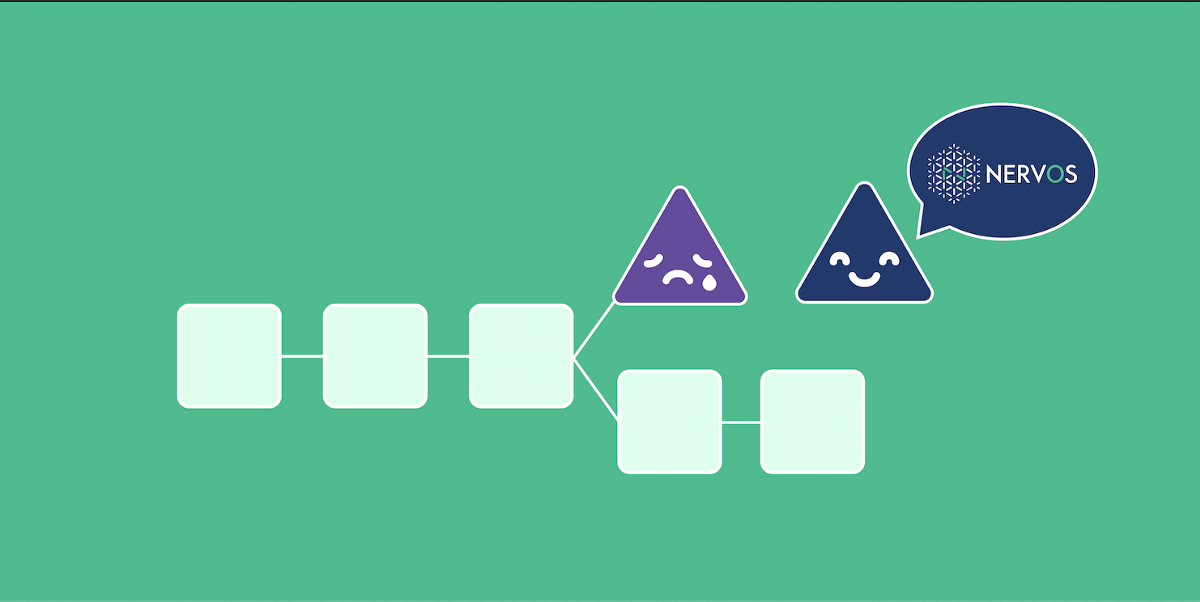
As the above picture shows, in NC when the selfish miner finds the block, it can immediately start mine the h+1 block, however, honest miners can only start after they receive the full block — that’s the selfish miner’s advantage during the block propagation period.
In NC-Max, when a selfish miner finds a block h, an honest miner can immediately start block h+1.
If the selfish miner wants to utilize this proposal without broadcasting transactions, it has to find blocks n block afterward, only then can the selfish miner utilize this advantage. However, this happens less often. You can not make sure that after 7 blocks there will be a block mined by me, it’s very hard to predict that.
2. Dynamic Block Interval and Block Reward to Best Utilize Bandwidth
NC-Max uses a different difficulty adjustment mechanism which targets a fixed orphan rate (counted as uncles in the last difficulty adjustment period):
If the orphan rate in the last difficulty period is below the target orphan rate, the difficulty will go down, the block interval will go down and the throughput will go up.
In other words, very few orphans mean that the network can synchronize transactions faster, which means we can increase the throughput without harming the decentralization.
Otherwise the difficulty increase, the block interval will increase and the throughput will decrease. A higher orphan rate means that the network can not process these many transactions in the difficulty adjustment period.
The block reward is proportional to the inverse of the expected block interval, so the expected total reward per difficulty adjustment period is fixed. For example: if we have 10 minutes per block, each block has 12.5 ; if we had 5 minutes per block, each block can have 6.125 . So the issue rate of the currency is always fixed.
3. Considering All Blocks in Difficulty Adjustment to Defend against Selfish Mining
In NC-Max, the difficulty adjustment mechanism counts all blocks, including uncles when estimating total power.
In NC, without the selfish attack, the attacker finds 3 blocks in 10, the honest miner finds 7. With the attack, the attacker finds 3 blocks in 7, the honest miners find 4, 3 honest blocks become orphaned, as the main chain grows slower, the difficulty lowers, the attacker can find more blocks with the same power.
In NC-Max, the difficulty will stay the same as the difficulty adjustment mechanism counts all blocks. The attacker can not find more blocks with the same power, therefore selfish is no longer profitable!
In conclusion, NC-Max makes use of orphaned blocks. We want to reduce the number of orphans by two-step transaction confirmation. After the orphan is reduced, we use the remaining ones as an indicator of bandwidth utilization to adjust the throughput, and given that the uncle information is embedded in the , we can use them to make selfish unprofitable (yeah!)
1.
2.
3. A detailed look into the design of NC-Max, a variant of Nakamoto Consensus with higher throughput.
P.S. NC-Max is a temporary name for Nervos consensus protocol — if you have any good idea on how it can be named please tell us in comments 🙂
Published at Thu, 07 Mar 2019 03:11:17 +0000


